Enterprise 5G Benefits
IOT & Connectivity
Software Engineering
Enterprise Verticals
Blogs

In this pack, we present how the combinations of LoRaWAN and 5G can be a winning combination. People will have heard about both, but will not have looked at them combined.
This paper is not meant to review and publish all LoRaWAN and 5G specs but solely focused where and how they complement.
This paper does not recommend certain implementations but its sole focus is on the technology itself.
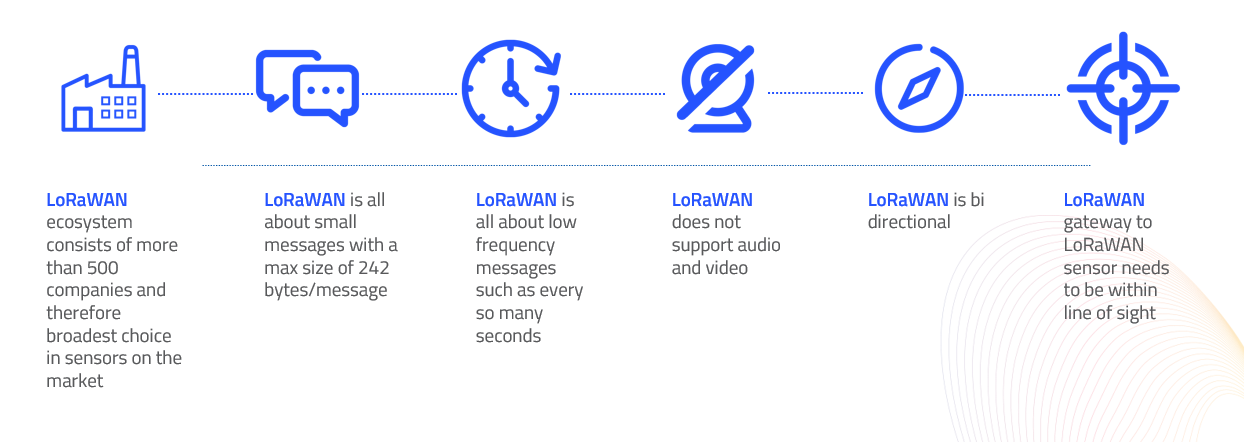
LoRaWAN protocol is a Low Power Wide Area Networking (LPWAN) communication protocol that functions on LoRa. The LoRaWAN specification is open so anyone can set up and operate a LoRa network.
LoRa is a wireless audio frequency technology that operates in a license-free radio frequency spectrum. LoRa is a physical layer protocol that uses spread spectrum modulation and supports long-range communication at the cost of a narrow bandwidth. It uses a narrow band waveform with a central frequency to send data, which makes it robust to interference.
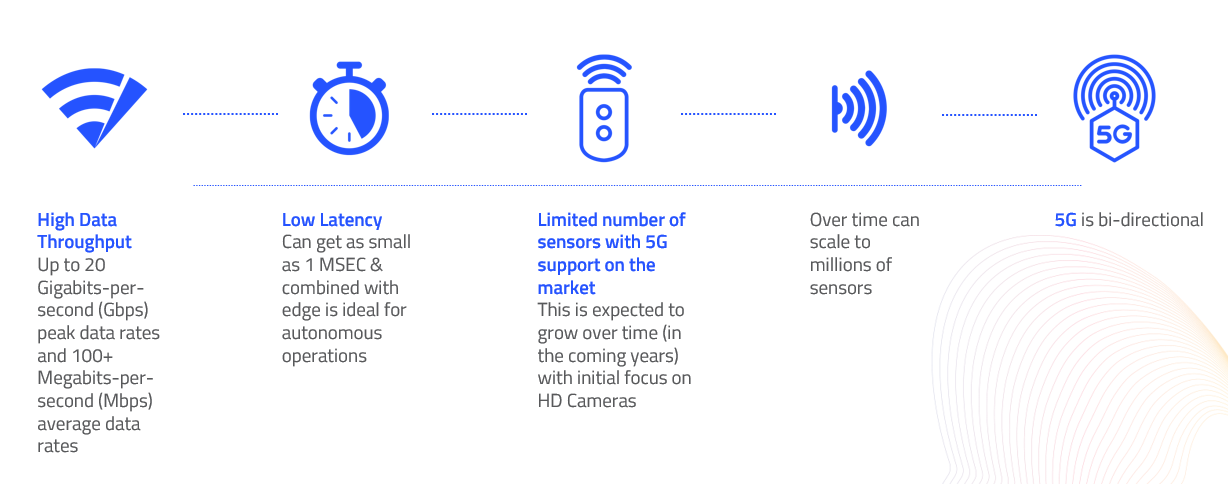
5G is the 5th generation of mobile network. It is a new global wireless standard after 1G, 2G, 3G, and 4G networks. 5G enables a new kind of network that is designed to connect virtually everyone and everything together including machines, objects, and devices.
5G wireless technology is meant to deliver higher multi-Gbps peak data speeds, ultra low latency, more reliability, massive network capacity, increased availability, and a more uniform user experience to more users. Higher performance and improved efficiency empower new user experiences and connects new industries.

LoRa Nodes / End Points: LoRa end points are the sensors or application where sensing and control takes place. These nodes are often placed remotely. Examples, sensors, tracking devices, etc.
LoRa Gateways: Unlike cellular communication where mobile devices are associated with the serving base stations, in LoRaWAN nodes are associated with a specific gateway. Instead, any data transmitted by the node is sent to all gateways and each gateway which receives a signal transmits it to a cloud based network server.
Typically, the gateways and network servers are connected via some backhaul (ideally 5G).
Network Servers: The networks server has all the intelligence. It filters the duplicate packets from different gateways, does security check, send ACKs to the gateways. In the end if a packet is intended for an application server, the network server sends the packet to the specific application server.
Using this type of network where all gateways can send the same packet to the network server, the need of hand-off or handover is removed. This is useful for asset-tracking application where assets move from one location to another.
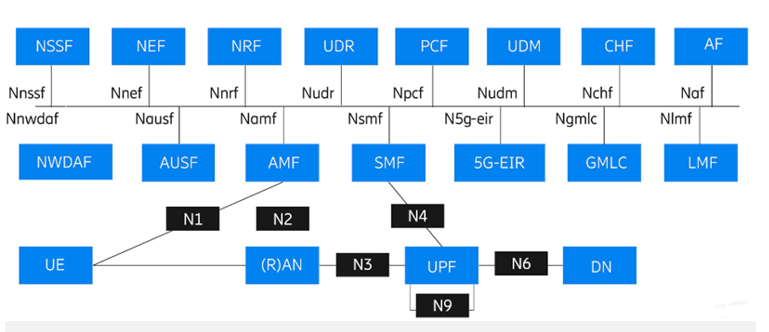
The new SGC architecture is based an what is called a Service-Based Architecture (SBA). which implements IT network principles and a cloud-native design approach. In this new architecture. each network function (NF) offers one or more services to other NFs via Application Programming Interfaces (API). Each NF is formed by a combination of small pieces of software code called as microservices.
Some microservices can even be re-used for different NFs. making implementation more effective and facilitating independent life-cycle management -which allows upgrades and new functionalities to be deployed with zero impact on running services.